图标点选验证码识别---python破解代码
开源地址:https://github.com/Bump-mann/simple_ocr
首先我们看一个较简单的图标点选验证码
请添加图片描述

从上面图片中依次点击以下图形
 |
 |
 |
请添加图片描述 请添加图片描述 请添加图片描述
笔者的思路(其实就是对着别人的抄)是先识别出图形切割下来,然后分别对比相似度,就可以得出需要点击位置啦~
模型下载链接放在文章末尾!
显而易见,识别分为两部分,以下为目标识别代码
'''
分割图标点选验证码图片的各个图标
'''
import os
import sys
import time
from io import BytesIO
import onnxruntime
import torch
import torchvision
import numpy as np
import cv2
# 图像处理
from PIL import Image
def padded_resize(im, new_shape=(640, 640), stride=32):
try:
shape = im.shape[:2]
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1]
# dw, dh = np.mod(dw, stride), np.mod(dh, stride)
dw /= 2
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
im = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=(114, 114, 114)) # add border
# Convert
im = im.transpose((2, 0, 1))[::-1] # HWC to CHW, BGR to RGB
im = np.ascontiguousarray(im)
im = torch.from_numpy(im)
im = im.float()
im /= 255
im = im[None]
im = im.cpu().numpy() # torch to numpy
return im
except:
print("123")
def xywh2xyxy(x):
# Convert nx4 boxes from [x, y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2] where xy1=top-left, xy2=bottom-right
y = x.clone() if isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) else np.copy(x)
y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2 # top left x
y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2 # top left y
y[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2 # bottom right x
y[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2 # bottom right y
return y
def box_iou(box1, box2):
"""
Return intersection-over-union (Jaccard index) of boxes.
Both sets of boxes are expected to be in (x1, y1, x2, y2) format.
Arguments:
box1 (Tensor[N, 4])
box2 (Tensor[M, 4])
Returns:
iou (Tensor[N, M]): the NxM matrix containing the pairwise
IoU values for every element in boxes1 and boxes2
"""
def box_area(box):
# box = 4xn
return (box[2] - box[0]) * (box[3] - box[1])
area1 = box_area(box1.T)
area2 = box_area(box2.T)
# inter(N,M) = (rb(N,M,2) - lt(N,M,2)).clamp(0).prod(2)
inter = (torch.min(box1[:, None, 2:], box2[:, 2:]) - torch.max(box1[:, None, :2], box2[:, :2])).clamp(0).prod(2)
return inter / (area1[:, None] + area2 - inter) # iou = inter / (area1 + area2 - inter)
def non_max_suppression(prediction, conf_thres=0.25, iou_thres=0.45, classes=None, agnostic=False, multi_label=False,
labels=(), max_det=300):
"""Runs Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) on inference results
Returns:
list of detections, on (n,6) tensor per image [xyxy, conf, cls]
"""
nc = prediction.shape[2] - 5 # number of classes
xc = prediction[..., 4] > conf_thres # candidates
# Checks
assert 0 <= conf_thres <= 1, f'Invalid Confidence threshold {conf_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
assert 0 <= iou_thres <= 1, f'Invalid IoU {iou_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
# Settings
min_wh, max_wh = 2, 7680 # (pixels) minimum and maximum box width and height
max_nms = 30000 # maximum number of boxes into torchvision.ops.nms()
time_limit = 10.0 # seconds to quit after
redundant = True # require redundant detections
multi_label &= nc > 1 # multiple labels per box (adds 0.5ms/img)
merge = False # use merge-NMS
t = time.time()
output = [torch.zeros((0, 6), device=prediction.device)] * prediction.shape[0]
for xi, x in enumerate(prediction): # image index, image inference
# Apply constraints
x[((x[..., 2:4] < min_wh) | (x[..., 2:4] > max_wh)).any(1), 4] = 0 # width-height
x = x[xc[xi]] # confidence
# Cat apriori labels if autolabelling
if labels and len(labels[xi]):
lb = labels[xi]
v = torch.zeros((len(lb), nc + 5), device=x.device)
v[:, :4] = lb[:, 1:5] # box
v[:, 4] = 1.0 # conf
v[range(len(lb)), lb[:, 0].long() + 5] = 1.0 # cls
x = torch.cat((x, v), 0)
# If none remain process next image
if not x.shape[0]:
continue
# Compute conf
x[:, 5:] *= x[:, 4:5] # conf = obj_conf * cls_conf
# Box (center x, center y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
box = xywh2xyxy(x[:, :4])
# Detections matrix nx6 (xyxy, conf, cls)
if multi_label:
i, j = (x[:, 5:] > conf_thres).nonzero(as_tuple=False).T
x = torch.cat((box[i], x[i, j + 5, None], j[:, None].float()), 1)
else: # best class only
conf, j = x[:, 5:].max(1, keepdim=True)
x = torch.cat((box, conf, j.float()), 1)[conf.view(-1) > conf_thres]
# Filter by class
if classes is not None:
x = x[(x[:, 5:6] == torch.tensor(classes, device=x.device)).any(1)]
# Apply finite constraint
# if not torch.isfinite(x).all():
# x = x[torch.isfinite(x).all(1)]
# Check shape
n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
if not n: # no boxes
continue
elif n > max_nms: # excess boxes
x = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)[:max_nms]] # sort by confidence
# Batched NMS
c = x[:, 5:6] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classes
boxes, scores = x[:, :4] + c, x[:, 4] # boxes (offset by class), scores
i = torchvision.ops.nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres) # NMS
if i.shape[0] > max_det: # limit detections
i = i[:max_det]
if merge and (1 < n < 3E3): # Merge NMS (boxes merged using weighted mean)
# update boxes as boxes(i,4) = weights(i,n) * boxes(n,4)
iou = box_iou(boxes[i], boxes) > iou_thres # iou matrix
weights = iou * scores[None] # box weights
x[i, :4] = torch.mm(weights, x[:, :4]).float() / weights.sum(1, keepdim=True) # merged boxes
if redundant:
i = i[iou.sum(1) > 1] # require redundancy
output[xi] = x[i]
if (time.time() - t) > time_limit:
break # time limit exceeded
return output
def xyxy2xywh(x):
# Convert nx4 boxes from [x1, y1, x2, y2] to [x, y, w, h] where xy1=top-left, xy2=bottom-right
y = x.clone() if isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) else np.copy(x)
y[:, 0] = (x[:, 0] + x[:, 2]) / 2 # x center
y[:, 1] = (x[:, 1] + x[:, 3]) / 2 # y center
y[:, 2] = x[:, 2] - x[:, 0] # width
y[:, 3] = x[:, 3] - x[:, 1] # height
return y
def is_ascii(s=''):
# Is string composed of all ASCII (no UTF) characters? (note str().isascii() introduced in python 3.7)
s = str(s) # convert list, tuple, None, etc. to str
return len(s.encode().decode('ascii', 'ignore')) == len(s)
def box_label(self, box, label='', color=(128, 128, 128), txt_color=(255, 255, 255)):
# Add one xyxy box to image with label
if self.pil or not is_ascii(label):
self.draw.rectangle(box, width=self.lw, outline=color) # box
if label:
w, h = self.font.getsize(label) # text width, height
outside = box[1] - h >= 0 # label fits outside box
self.draw.rectangle((box[0],
box[1] - h if outside else box[1],
box[0] + w + 1,
box[1] + 1 if outside else box[1] + h + 1), fill=color)
# self.draw.text((box[0], box[1]), label, fill=txt_color, font=self.font, anchor='ls') # for PIL>8.0
self.draw.text((box[0], box[1] - h if outside else box[1]), label, fill=txt_color, font=self.font)
else: # cv2
p1, p2 = (int(box[0]), int(box[1])), (int(box[2]), int(box[3]))
cv2.rectangle(self.im, p1, p2, color, thickness=self.lw, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
if label:
tf = max(self.lw - 1, 1) # font thickness
w, h = cv2.getTextSize(label, 0, fontScale=self.lw / 3, thickness=tf)[0] # text width, height
outside = p1[1] - h - 3 >= 0 # label fits outside box
p2 = p1[0] + w, p1[1] - h - 3 if outside else p1[1] + h + 3
cv2.rectangle(self.im, p1, p2, color, -1, cv2.LINE_AA) # filled
cv2.putText(self.im, label, (p1[0], p1[1] - 2 if outside else p1[1] + h + 2), 0, self.lw / 3, txt_color,
thickness=tf, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
def return_coordinates(xyxy, conf):
conf = float(conf.numpy())
gain = 1.02
pad = 10
xyxy = torch.tensor(xyxy).view(-1, 4)
b = xyxy2xywh(xyxy) # boxes
b[:, 2:] = b[:, 2:] * gain + pad # box wh * gain + pad
xyxy = xywh2xyxy(b).long()
c1, c2 = (int(xyxy[0, 0]) + 6, int(xyxy[0, 1]) + 6), (int(xyxy[0, 2]) - 6, int(xyxy[0, 3]) - 6)
# print(f"leftTop:{c1},rightBottom:{c2},Confidence:{conf*100}%")
result_dict = {"leftTop": c1, "rightBottom": c2, "Confidence": conf}
return result_dict
def clip_coords(boxes, shape):
# Clip bounding xyxy bounding boxes to image shape (height, width)
if isinstance(boxes, torch.Tensor): # faster individually
boxes[:, 0].clamp_(0, shape[1]) # x1
boxes[:, 1].clamp_(0, shape[0]) # y1
boxes[:, 2].clamp_(0, shape[1]) # x2
boxes[:, 3].clamp_(0, shape[0]) # y2
else: # np.array (faster grouped)
boxes[:, [0, 2]] = boxes[:, [0, 2]].clip(0, shape[1]) # x1, x2
boxes[:, [1, 3]] = boxes[:, [1, 3]].clip(0, shape[0]) # y1, y2
def scale_coords(img1_shape, coords, img0_shape, ratio_pad=None):
# Rescale coords (xyxy) from img1_shape to img0_shape
if ratio_pad is None: # calculate from img0_shape
gain = min(img1_shape[0] / img0_shape[0], img1_shape[1] / img0_shape[1]) # gain = old / new
pad = (img1_shape[1] - img0_shape[1] * gain) / 2, (img1_shape[0] - img0_shape[0] * gain) / 2 # wh padding
else:
gain = ratio_pad[0][0]
pad = ratio_pad[1]
coords[:, [0, 2]] -= pad[0] # x padding
coords[:, [1, 3]] -= pad[1] # y padding
coords[:, :4] /= gain
clip_coords(coords, img0_shape)
return coords
def onnx_model_main(path):
# onnx
session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession("./models/图标点选_分割图片.onnx", providers=["CPUExecutionProvider"])
start = time.time()
image = open(path, "rb").read()
img = np.array(Image.open(BytesIO(image)))
# img = cv2.imread(path)
# 图像处理
img = img[:, :, :3]
im = padded_resize(img)
# 模型调度
pred = session.run([session.get_outputs()[0].name], {session.get_inputs()[0].name: im})[0]
pred = torch.tensor(pred)
pred = non_max_suppression(pred, conf_thres=0.6, iou_thres=0.6, max_det=1000) # 大于百分之六十的置信度
coordinate_list = []
for i, det in enumerate(pred):
det[:, :4] = scale_coords(im.shape[2:], det[:, :4], img.shape).round()
for *xyxy, conf, cls in reversed(det):
# 返回坐标和置信度
coordinates = return_coordinates(xyxy, conf)
print(coordinates)
coordinate_list.append(coordinates)
# 坐标列表
coordinate = sorted(coordinate_list, key=lambda a: a["Confidence"])
data_list = []
# 用时
duration = str((time.time() - start))
if len(coordinate) == 0:
data = {'message': 'error', 'time': duration}
else:
# coordinate = coordinate[-1]
for coordinate in coordinate_list:
x = coordinate.get('leftTop')[0]
y = coordinate.get('leftTop')[1]
w = coordinate.get('rightBottom')[0] - coordinate.get('leftTop')[0]
h = coordinate.get('rightBottom')[1] - coordinate.get('leftTop')[1]
point = f"{x}|{y}|{w}|{h}"
data = {'message': 'success', 'time': duration, 'point': point}
data.update(coordinate)
data_list.append(data)
print(data_list)
return data_list
def drow_rectangle(coordinate, path):
import os
if "new_%s" % path in os.listdir('./'):
img = cv2.imread("new_%s" % path)
else:
img = cv2.imread(path)
# 画框
result = cv2.rectangle(img, coordinate.get("leftTop"), coordinate.get("rightBottom"), (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.imwrite("new_%s" % path, result) # 返回圈中矩形的图片
print("返回坐标矩形成功")
# python install pillow
# 分割图片
def cut_image(image, point, name):
lists = point.split('|')
box = (int(lists[0]), int(lists[1]), int(lists[2]) + int(lists[0]), int(lists[3]) + int(lists[1]))
images = image.crop(box)
images.save('{}.png'.format(name), 'PNG')
from os import path
def scaner_file(url):
lists = []
# 遍历当前路径下所有文件
file = os.listdir(url)
for f in file:
# 字符串拼接
# real_url = path.join (url , f)
# 打印出来
# print(real_url)
lists.append([url, f])
return lists
# Hash值对比
def cmpHash(hash1, hash2,shape=(10,10)):
n = 0
# hash长度不同则返回-1代表传参出错
if len(hash1)!=len(hash2):
return -1
# 遍历判断
for i in range(len(hash1)):
# 相等则n计数+1,n最终为相似度
if hash1[i] == hash2[i]:
n = n + 1
return n/(shape[0]*shape[1])
# 均值哈希算法
def aHash(img,shape=(10,10)):
# 缩放为10*10
img = cv2.resize(img, shape)
# 转换为灰度图
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# s为像素和初值为0,hash_str为hash值初值为''
s = 0
hash_str = ''
# 遍历累加求像素和
for i in range(shape[0]):
for j in range(shape[1]):
s = s + gray[i, j]
# 求平均灰度
avg = s / 100
# 灰度大于平均值为1相反为0生成图片的hash值
for i in range(shape[0]):
for j in range(shape[1]):
if gray[i, j] > avg:
hash_str = hash_str + '1'
else:
hash_str = hash_str + '0'
return hash_str
'''
以下是测试代码
'''
if __name__ == '__main__':
#图片路径
path = r'C:\Users\qiu_feng\Desktop\d1e81bb61df84abfaa41ae92a5e6c787.jpg'
coordinate_onnx = onnx_model_main(path)
num = 0
for j in coordinate_onnx:
num += 1
image = Image.open(path) # 读取图片
name = path[:-4:] + '__切割后图片_' + str(num)
cut_image(image, j['point'], name)
效果如下:
在这里插入图片描述

有些龟裂是因为我加了一些自以为可以“提高”识别效果的东西…
以下是相似度代码
'''
图片相似度对比 适用于图标点选
'''
import os
import cv2
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from .nets.siamese import siamese
from .utils.utils import letterbox_image, preprocess_input, cvtColor, show_config
# -----------nets----------------------------------------#
# 使用自己训练好的模型预测需要修改model_path参数
# ---------------------------------------------------#
class Siamese(object):
_defaults = {
# -----------------------------------------------------#
# 使用自己训练好的模型进行预测一定要修改model_path
# model_path指向logs文件夹下的权值文件
# -----------------------------------------------------#
"model_path": './models/图标点选_相似度.h5',
# -----------------------------------------------------#
# 输入图片的大小。
# -----------------------------------------------------#
"input_shape": [60, 60],
# --------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 该变量用于控制是否使用letterbox_image对输入图像进行不失真的resize
# 否则对图像进行CenterCrop
# --------------------------------------------------------------------#
"letterbox_image": True,
}
@classmethod
def get_defaults(cls, n):
if n in cls._defaults:
return cls._defaults[n]
else:
return "Unrecognized attribute name '" + n + "'"
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 初始化Siamese
# ---------------------------------------------------#
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.__dict__.update(self._defaults)
for name, value in kwargs.items():
setattr(self, name, value)
self.generate()
show_config(**self._defaults)
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 载入模型
# ---------------------------------------------------#
def generate(self):
model_path = os.path.expanduser(self.model_path)
assert model_path.endswith('.h5'), 'Keras model or weights must be a .h5 file.'
# ---------------------------#
# 载入模型与权值
# ---------------------------#
self.model = siamese([self.input_shape[0], self.input_shape[1], 3])
self.model.load_weights(self.model_path)
print('{} model loaded.'.format(model_path))
@tf.function
def get_pred(self, photo):
preds = self.model(photo, training=False)
return preds
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 检测图片
# ---------------------------------------------------#
def detect_image(self, image_1, image_2):
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 在这里将图像转换成RGB图像,防止灰度图在预测时报错。
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
image_1 = cvtColor(image_1)
image_2 = cvtColor(image_2)
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 对输入图像进行不失真的resize
# ---------------------------------------------------#
image_1 = letterbox_image(image_1, [self.input_shape[1], self.input_shape[0]], self.letterbox_image)
image_2 = letterbox_image(image_2, [self.input_shape[1], self.input_shape[0]], self.letterbox_image)
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 归一化+添加上batch_s ize维度
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
photo1 = np.expand_dims(preprocess_input(np.array(image_1, np.float32)), 0)
photo2 = np.expand_dims(preprocess_input(np.array(image_2, np.float32)), 0)
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 获得预测结果,output输出为概率
# ---------------------------------------------------#
output = np.array(self.get_pred([photo1, photo2])[0])
# plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
# plt.imshow(np.array(image_1))
#
# plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
# plt.imshow(np.array(image_2))
# plt.text(-12, -12, 'Similarity:%.3f' % output, ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=11)
# plt.show()
return output
'''
以下是测试代码 (本来想着在每个代码下面加测试来着,但是认为不好就废弃掉了)
'''
if __name__ == '__main__':
gpus = tf.config.experimental.list_physical_devices(device_type='GPU')
for gpu in gpus:
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(gpu, True)
model = Siamese()
for i in range(1,6):
image_1 = Image.open('../test/图标点选/背景图__切割后图片_{}.png'.format(i))
max = 0
for j in range(1,4):
image_2 = Image.open('../test/图标点选/图形_{}.png'.format(j))
probability = model.detect_image(image_1, image_2)
#相似度低的就直接排除了
if probability[0] >0.5:
print('背景图__切割后图片_{}.png'.format(i),'和','图形_{}.png'.format(j),'相似度为:',probability)
# print(image_1_name,'和',image_2_name,'相似度最高')
效果如下
在这里插入图片描述
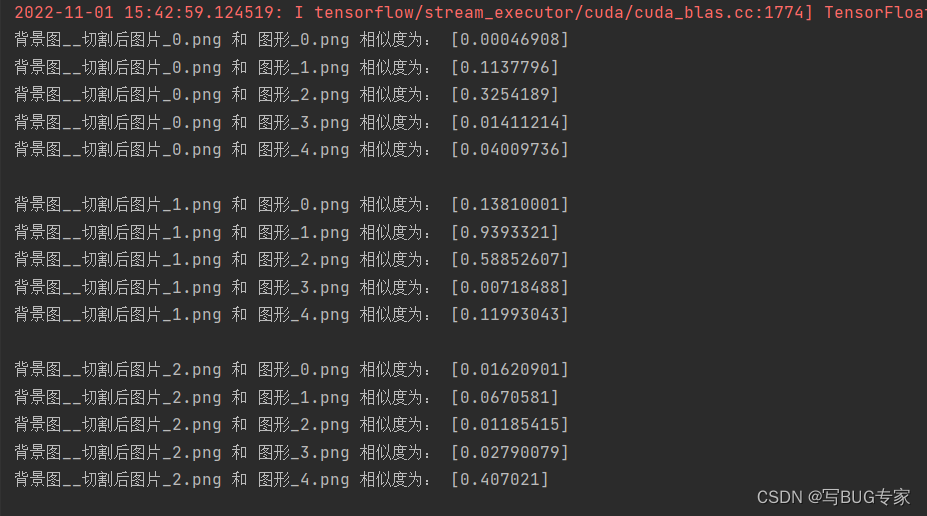
这样我们就知道每个图形的坐标及与相似度,即可得到点击坐标啦~
效果图如下

